
the body shape was more ape-like than humans, but differed from living African apes in a number of significant features.males were only slightly larger than females.The most complete specimen, a female, stood about 120cm tall similar in size to modern chimpanzees.about 300-350cc, similar in size to modern female chimpanzees and bonobos.Features of the anatomy are extremely primitive. This species was a facultative biped and stood upright on the ground but could move on all four limbs in trees. This species was originally classified as Australopithecus ramidus in 1994, but was reclassified in 1995 because its discoverers believed it was distinct enough to be placed into a new genus, Ardipithecus. It also offers new insights into how we evolved from the common ancestor we share with chimps. Even if Ardipithecus ramidus is not on our direct line, it must have been closely related to the direct ancestor and probably similar in appearance and adaptation. The discovers think it was ancestral to Australopithecus - it is the only putative hominin in evidence between 5.8 and 4.4 million years ago - but others do not agree. This species position as a direct ancestor of humans is unclear and scientists are still debating where it should be placed relative to our direct line. Additional fossils that may also belong to this species have been collected in northern Kenya. Distributionįossils belonging to this species were found in eastern Africa in the Middle Awash valley, Ethiopia. The name ‘ramid’ means ‘root’ in the Afar language. ‘Ardi’ means ‘ground’ or ‘floor’ and ‘pithecus’ is Latinised Greek for ‘ape’.
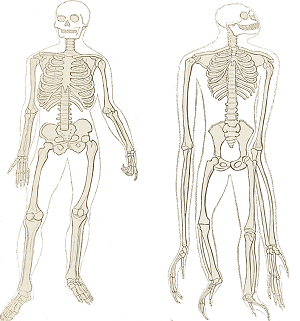
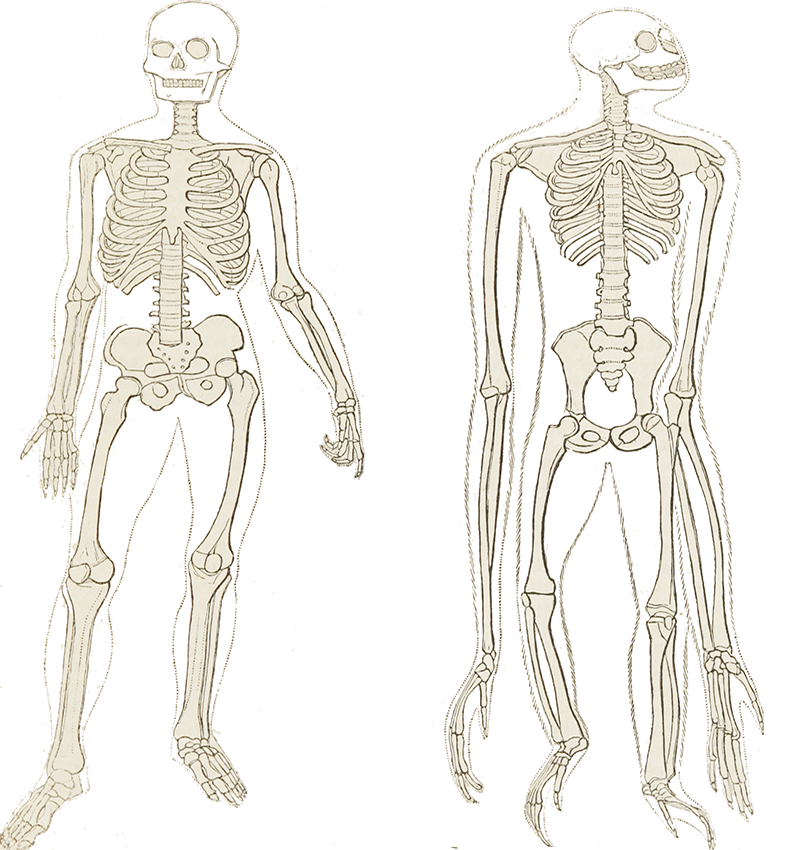
The name is derived from the local Afar language. It also indicates that chimpanzee evolution underwent high degrees of specialisation since diverging from the last common ancestor and thus these apes are poor models for understanding the appearance of this ancestor. Analysis of the skeleton reveals that humans did not evolve from knuckle-walking apes, as was long believed. Instead, it may well preserve some of the characteristics of the last chimp-human ancestor. The skeleton does not look much like a chimp or gorilla or have the expected 'transitional' features. The results were hugely significant in terms of how we view the evolution of the earliest hominins and the physical appearance of the last common ancestor of humans and chimpanzees. She weighed about 50kg and stood about 120cm tall.The skeleton was in extremely poor condition and it took the team 15 years to excavate, scan, make virtual reconstructions, assemble and then analyse. The individual is believed to be a female and is nicknamed ‘Ardi’. It is the oldest known skeleton of a human ancestor.
ARA-VP-6/1 teeth: This is the holotype for this species.Some specimens discovered earlier in Kanapoi, Lothagam and Tabarin could also belong to this species. The remains mostly consist of teeth and jaw fragments, but also some bones from the hands and feet. In 2005, the remains of 9 individuals were recovered from As Duma in northern Ethiopia. A partial humerus (arm bone) indicates that this species was smaller than the average Australopithecus afarensis. Most of the remains are dental, but some skull and limb bones were also found. The finds number over 110 specimens and represent about 35 individual members of this species.

Hundreds of pieces of fossilised bone were recovered during 1992-1994, all from localities west of the Awash River, in Aramis, Ethiopia. 4.4 to 4.2 million years ago Important fossil discoveries


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
